By Carolyn Cui and Julie Wernau

There is nary a corner on Earth where investors won’t journey to find extra yield. But the trip to Mongolia is proving treacherous.
Money managers piled into assets from the world’s most sparsely populated country in past years on the prospects of vast untapped mines rich with copper and gold. Mongolian debt got an additional boost this year, soaring 6% in July, as raw-material prices picked up and investors sought alternatives to low and even negative bond yields in developed countries.
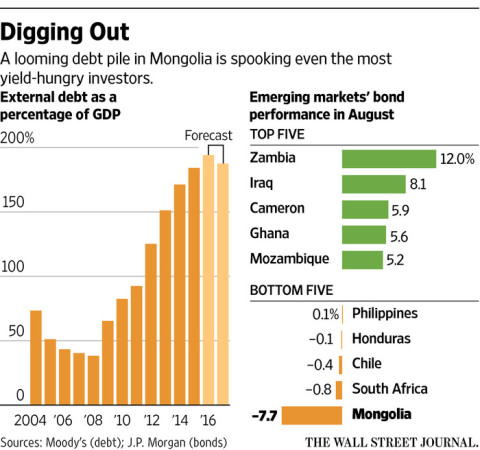
But in August, Mongolia’s finance minister stunned global investors by saying that its government debt would reach 78% of the gross domestic product, far above the country’s 55% target. The revelation triggered a selloff in Mongolia’s markets, with the country’s dollar-denominated debt tumbling 7.7% last month and the nation’s currency falling the most among all its developing-economy peers, before rebounding slightly this month.
Mongolia is among a handful of countries with once-bright futures that took on massive debt loads during a period of investor enthusiasm for frontier markets. In 2011, the nation was the world’s fastest-growing economy, expanding at a 17% rate as prices of copper, gold and iron ore soared.
Foreign lenders handed over billions of dollars to the government, its banks and mining companies to help extract wealth from underground. Among the bonds’ holders are BlackRock Inc., Franklin Templeton, Goldman Sachs Group Inc. and UBS Global Asset Management, according to the latest holder data from Thomson Reuters. Mongolia’s debt levels swelled 264% in the five years ended 2015, the largest increase in the world during that period, according to Moody’s Investors Service.
But the commodities bust that began in 2011 crimped the country’s growth. Now, the prospect of higher U.S. interest rates, which could make bonds in developing economies less attractive, could worsen a troubled situation.
As of the first quarter, Mongolia’s total debt owed to foreign creditors stood at $22.6 billion, compared with a still tiny $11.8 billion economy. Meanwhile, a $580 million Mongolian bond taken on to help finance a still-unfinished project to connect 21 provinces with roads comes due in 2017, part of $2 billion in maturing public- and private-sector debt in 2017, according to the International Monetary Fund.
Investors are pinning hopes on a vast gold and copper mine that is expected to lead to massive economic growth. In December 2015, the government approved a $4.4 billion financing deal for Rio Tinto PLC’s second phase of the Oyu Tolgoi copper and gold mine, believed to be the world’s largest underdeveloped reserve of copper, concluding a four-year-long negotiation. But delays in the projects have been costly: During the wait, copper prices more than halved.
As the country’s current financial woes deepened, the government resorted to emergency measures. In August, the government said it may soon stop paying its civil servants and the military and raised interest rates by 4.5 percentage points to combat capital outflows.
Moody’s also lowered Mongolia’s sovereign credit rating, sending it further into junk status. Standard & Poor’s made a similar move.
If Mongolia turns to the International Monetary Fund for help, that could prop up investor confidence that it will be able to pay its debt, said Kevin Daly, a portfolio manager at Aberdeen Asset Management, with $9 billion in emerging-market debt under management, including Mongolian bonds. The IMF visited the country in August.
The selloff in Mongolia contrasts with the broad rally in emerging markets. Nearly $80 billion went into emerging markets during the first eight months of this year, the Institute of International Finance said. Emerging-market dollar-denominated debt returned 14.7% this year through August.
But if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, reducing liquidity in the global financial system, countries that rely on a single commodity or struggle with economic data transparency “represent the first level of risks,” said Jim Barrineau, co-head of emerging markets debt at Schroder Investment Management Ltd., which has £343.8 billion ($456.19 billion) of assets under management.
Copper made up 49% of Mongolia’s exports in 2015, according to the United Nations International Trade Statistics Yearbook.
“Given overall market conditions and the assumptions around the IMF, I think perhaps the investors would continue to give them the benefit of the doubt,” said Kathryn Exum, a sovereign analyst at Gramercy Funds Management LLC. “But from an overall fundamental perspective, it’s too expensive. Mongolia and some of the weaker credits will sell off much more significantly if a hawkish Fed returns.”
Write to Carolyn Cui at carolyn.cui@wsj.com and Julie Wernau at Julie.Wernau@wsj.com