Though she had no intention of being funny, we laughed out loud, as undoubtedly many did with us, when incumbent and wannabe IMF head Christine Lagarde said last week in Davos that China has a communication issue. Of course, Lagarde knows full well that Beijing has much bigger problems than communication ‘with the market’. Or, to put it differently, if Xi and Li et al would ‘improve’ their communication by telling the truth about their economy, nobody would be talking about communication anymore.
Mixed signals from China, which is attempting to shift its economy away from exports and investment to a consumer-driven model, have deepened concerns about the outlook for world growth, she said. Uncertainty is “something that markets do not like”, Ms Lagarde told a panel of business leaders and economic regulators in the snow-blanketed Swiss ski resort. Investors have struggled with “not knowing exactly what the policy is, not knowing exactly against what the renminbi is going to be valued”, she said, referring to China’s currency. “I think better and more communication will certainly serve that transition better.”The world’s second-largest economy this week announced its 2015 GDP growth as 6.9%, its slowest in a quarter of a century. The figure cast a shadow over the summit, where IHS chief economist Nariman Behravesh told AFP that Chinese policymakers had “fumbled” and had “added to the uncertainty and the volatility by their behaviour”. Mr Fang Xinghai, the vice-chairman of China’s securities regulator, said at the same panel that “in terms of communication, we should do a better job”. “We have to be patient because our system is not structured in a way that is able to communicate seamlessly with the market,” he added.
The real issue is what people would think if Beijing announced a more realistic 2% or less GDP growth number. The thought alone scares Lagarde as much as anyone, including the Politburo. The sole option seems to be to keep lying as long as you can get away with it. But how and where the yuan will be valued by China itself has become entirely inconsequential compared to how markets value the currency.
The PBoC spent a fortune trying to straighten the offshore and onshore yuan(s), only to see the two diverge sharply again, as Shanghai stocks posted the biggest loss on Tuesday, at 6.4%, since the ‘unfortunate’ circuit breaker incident. That puts additional pressure on the Hong Kong dollar peg, and ultimately on the mainland China peg to whatever it is they’re trying to peg to.
Beijing might solve some of these problems by devaluing the yuan by 30%, or even 50%, but it would invite a large amount of other problems in the door if it did. Like a full-blown currency war. Still, it’s just a matter of time till Xi and Li either do it voluntarily or are forced to by ‘the market’.
What they are trying very hard NOT to communicate is how much pain their Ponzi debt burden has put them in. It’s not even fully clear to what extent Xi himself is aware of this, but he knows at least enough to keep his mouth shut on the topic. It’s quite possible that some of his top aides dare not reveal the real tally to their boss for fear of their jobs and heads.
In concert with denial and obfuscation, pride and hubris may be clouding the image the Chinese have of themselves and their economy. The rest of the world has followed them in that to a large degree, but it’s got to wake up at some point. If what the WSJ quotes a Beijing-based investor as saying is halfway true, and Xi realizes the opportunity it provides him, a huge devaluation may be imminent after all, if Shanghai shares keep falling the way they are.
Yuan’s Fall Is Just ‘Noise’ Amid Deeper China Woes
The country is already littered with “zombie” factories, empty apartment blocks that form ghostly suburbs, mothballed power stations and other infrastructure that nobody needs. But yet more wasteful projects are in the pipeline, even as the government talks about cutting industrial overcapacity. “That’s the misalignment—everything else is noise,” says Rodney Jones, the Beijing-based principal of Wigram Capital Advisors, who was a partner at Soros Fund Management during the 1990s. If debt keeps piling up at the current rate, China faces an eventual financial crisis, perhaps leading to years of subpar growth, mirroring the fate of Japan after its bubble burst in the early 1990s.Mr. Jones argues that global equity markets haven’t property adjusted to this risk, even after a 16% decline in U.S. dollar terms from their May peak. “The world will have to learn to live without demand from China,” he says. “It’ll come as a shock.” A sharp devaluation won’t fix these distortions, and might even make matters worse if, as likely, it were to trigger financial mayhem in China’s trading partners. An alternative—further clamping cross-border currency controls—would be a humiliating retreat from Beijing’s policy of making the yuan more international.
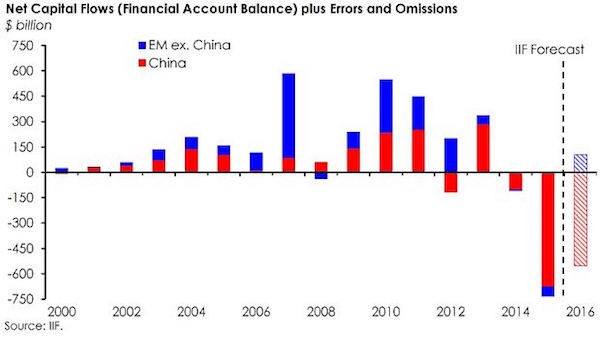
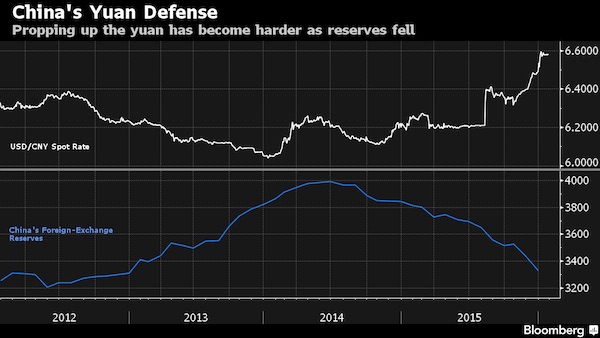
If China imports continue to fall the way they have recently, a development that has already relentlessly hammered global commodities markets and exporting emerging nations, the advantages of a large devaluation could become irresistible even for a proud president. With capital flight in 2015 estimated at $1 trillion, and a roughly equal chunk of foreign reserves thrown at attempts to ‘stabilize’ the yuan, that pride is getting costly.
Might as well swallow the bitter pill in one go then and get it over with?! It would make exports much more attractive at a time when more expensive imports are much less of an issue. As nice example is the very disappointing sales of iPhones in the country, prompting this comment from Apple CEO Tim Cook today: “We’re seeing extreme conditions unlike anything we’ve experienced before just about everywhere we look.” I think he might want to consider that what happened before was extreme, not what is now.
Beijing did a few things recently that triggered my cynicism radar. First, they targeted George Soros.
China Accuses George Soros Of ‘Declaring War’ On Yuan
Chinese state media has stepped up a salvo of biting commentaries against George Soros and other currency traders as the yuan comes under pressure, with the billionaire investor accused of “declaring war” on the unit. At the annual World Economic Forum in Davos last week, Soros told Bloomberg TV that the world’s second-largest economy was heading for more troubles. “A hard landing is practically unavoidable,” he said. Soros [..] pointed to deflation and excessive debt as reasons for China’s slowdown.[..] Soros “publicly ‘declared war’ on China”, the paper said, citing the 85-year-old as saying that he had taken positions against Asian currencies. But some readers questioned whether the official rhetoric could fuel Chinese investors’ fears. “They say a lot of loud slogans, but do official media even know that Chinese investors are in hell?” said one poster on social media network Weibo. “I’m afraid that Chinese investors will die in a stampede before Soros even shows his hand.”
And I’m thinking: why should you go after Soros in a very public way when you know the whole world will take note and there’s nothing you can do other than stomp your feet and thump your chest? “Look, everyone, the world’s most notorious and successful short seller is after us, but we’re so much smarter!” Maybe they think Chinese mom and pop investor juggernauts will fall for their ‘whatever it takes’ tale, but they have to deal with the entire planet here.
Could this be simple stupidity? At a certain point that gets hard to believe. An even better example, and one that is really brow-raising, was the announcement of an inquiry into China’s statistics chief:
Head Of China’s Statistics Bureau Investigated For Corruption
The head of China’s statistics bureau is being investigated for corruption, the country’s watchdog said on Tuesday. “Wang Baoan is suspected of severe disciplinary violations, he is currently under investigation,” the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection said in a one-line statement on its website, using a phrase that is usually used to refer to corruption. The announcement came just hours after Wang appeared at a media briefing in Beijing on China’s economy in 2015. Last week the National Bureau of Statistics released data that showed China’s economy grew at the slowest pace in 25 years. Wang reiterated on Tuesday that the country’s GDP calculations were reliable, Chinese media reported, despite widespread criticism of the data.
Here’s a guy seeking to soothe his audience, which in present circumstances includes the whole globe, and you cut him off at the knees just hours after? He says all’s fine, and then you sent a message to the world that he can’t be trusted?
The timing seems crucial here. They could have waited a week, or two, so the connection between the two events (Wang’s statement and the inquiry announcement) would have been much less obvious. They could also, of course, have had the inquiry but kept it hush-hush. Instead, as in the Soros case, there’s a big public declaration.
Wang is head of a statistics bureau that, says the NYT, is tasked with:
Inquiry in China Adds to Doubt Over Reliability of Economic Data
The statistics bureau has a variety of responsibilities that are hard to balance even in the best of times. The bureau is supposed to provide China’s leaders with an unvarnished assessment of the country’s economic strengths and weaknesses, even while reassuring the public about growth and maintaining consumer confidence. It is also supposed to release enough detailed and accurate information for investors and corporate leaders to make sound decisions about economic and financial prospects.
That leads us right back to the start of this article. Wang must provide “enough detailed and accurate information” for investors”, but how can he do that if the real numbers are as bad as I strongly think they are? In that case, accurate information would drive most investors away and drive others towards shorting the yuan.
He must also “provide China’s leaders with an unvarnished assessment of the country’s economic strengths and weaknesses”, and perhaps he screwed up there (too much varnish). Xi may have found out something real bad that Wang didn’t tell him about. But even then, the fact stands that Xi risks triggering exactly what he pretends to want to prevent, by taking this to the press.
To summarize: yes, it’s possible that Beijing has a communication problem. I’ve never had the idea that Xi understands that now his power dream has come true, he finds that power is not absolute, if and when he wishes to have a financial market that allows for China to get richer through trade. That he realizes the price to pay for that is having much less than total control.
Still, after glancing through this stuff, I wouldn’t be at all surprised if the decision for a very substantial devaluation of the yuan has already been taken. It would be a panic move, with largely unpredictable consequences, but then Beijing has plenty to panic about.
And I can’t wait to see what Lagarde has to say when she figures out her new currency basket baby turns around to bite her in the ass.



PS: Something I scribbled last week: Time and again, I see ‘experts’ claim that the fact that the Chinese services sector now makes up half of GDP, is a positive. But, even if we forget for now that much of its growth is due to financial services, the real meaning is the opposite. The services sector has been able to become so important simply because the manufacturing sector is plunging as badly as it is.