By Spiegel Online
There was a time when the German chancellor and the head of the European Central Bank had nice things to say about each other. Mario Draghi spoke of a “good working relationship,” while Angela Merkel noted “broad agreement.” Draghi, said Merkel, is extremely supportive “when it comes to European competitiveness.”
These days, though, meetings between the two most powerful politicians in the euro zone are often no different than their face-to-face at the most recent summit in Brussels. She observed that his forced policy of cheap money is endangering the business model of Germany’sSparkassen savings banks and retirement insurance companies. He snarled back that the sectors would simply have to adapt, just as the American financial sector has.
The alienation between Germany and the ECB has reached a new level. Back in deutsche mark times, Europeans often joked that the Germans “may not believe in God, but they believe in the Bundesbank,” as Germany’s central bank is called. Today, though, when it comes to relations between the ECB and the German population, people are more likely to speak of “parallel universes.”
ECB head Draghi doesn’t understand why he is getting so much resistance from the country that has profited from the euro more than any other. Yet Germans blame Draghi for miniscule yields on savings accounts and life/retirement insurance policies. Frustration is growing.
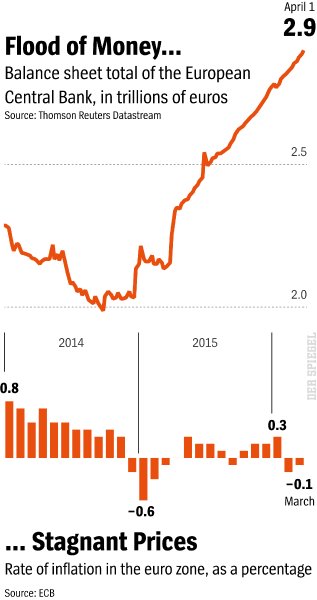
Draghi has pushed the prime rate down to zero and now even charges commercial banks a fee for parking their money at the ECB. He has also bought almost €2 trillion worth of bonds from euro-zone member states, making the ECB one of the largest state creditors of all time.
During his most recent appearance before the Frankfurt reporter pool, he went even further. The idea of pumping money directly into the economy, he said, was a “very interesting concept,” with a helicopter to distribute the money across the country if necessary, as economists have half-jokingly recommended. Doing so is seen as a way of boosting the economy. German money being thrown out of a helicopter: It would be difficult to find a more fitting image to show people that the money they have set aside for retirement may soon be worth very little.
Public Ruminations
The criticism of Draghi had already been significant, but his public ruminations about so-called “helicopter money” have magnified it to extreme levels. Even economists that tend to back the ECB, such as Peter Bofinger, who is one of Merkel’s economic advisors, are now accusing Draghi of constantly “pulling new rabbits out of the hat.” Leading representatives of the banking and insurance sectors are openly speaking of legal violations. And strategists within Merkel’s governing coalition, which pairs her conservatives with the center-left Social Democrats (SPD), are concerned that Draghi is handing the right-wing populist Alternative for Germany (AfD) yet another issue where they can score points with the voters. There is hardly any other issue that enrages Germans at town meetings and political party conventions as much as the disappearance of their savings due to the “unconventional measures” adopted by the ECB in Frankfurt.
By now, the growing dismay has been registered in the Chancellery. Merkel is also critical of Draghi’s zero percent interest policy, but she is afraid of making public demands that she may not be able to push through. Still, she is convinced that Draghi must give greater weight to German concerns, so she has resorted to telephone conversations and closed-door meetings to make her case.
Economics Minister Sigmar Gabriel, who is also head of the SPD and vice chancellor, has likewise refrained from publicly criticizing Draghi. Instead, he says it was the “inaction of European heads of government” that has transformed the ECB into “a kind of faux economic government.” But Draghi’s most recent decision to make money in the euro zone even cheaper has been heavily criticized within Gabriel’s Economics Ministry. “It jeopardizes the trust of all those who work hard to establish a small degree of prosperity or a nest-egg for retirement,” says one ministry official. “Plus, the cheap money hasn’t helped get the economy back on track.”
Most dangerous for Draghi, however, is the displeasure from the German Finance Ministry. A few weeks ago, Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble warned the ECB head that his ultra-loose monetary policies could “ultimately end in disaster.” The fact that Schäuble said anything at all is rather surprising, as were the words he chose. Out of respect for the ECB’s independence, finance ministers tend not to comment on decisions made by the central bank.
The Legal Boundary
But Schäuble believes Draghi’s course is calamitous. He is concerned that the unchecked creation of money could lead to new bubbles on the financial markets. Furthermore, negative interest rates have a negative impact on the profit margins of commercial banks — and part of the ECB’s mission is ensuring the stability of such banks. Schäuble believes that Draghi’s policies create misguided incentives for the governments of euro-zone member states.
To be sure, ECB independence is also of vital importance to Schäuble as well. But that is no longer the case when the bank’s policies exceed its legal mandate. It is a boundary that Schäuble believes Draghi and his people have crossed, which explains why the minister does not have a bad conscience about abandoning traditional reserve. “We have to initiate this dialogue about monetary policy,” says a Finance Ministry official.
Were the ECB, as Draghi has indicated it might, to open the monetary policy gates even wider — with, for example, helicopter money — the German finance minister would view it as a breaking point. Such a policy would see the ECB bypass the banking sector and distribute money directly to companies, consumers or states, all of which would stand in violation of the central bank’s own statutes. Should it come to that, sources in the German Finance Ministry say, Berlin would have to consider taking the ECB to court to clarify the limits of its mandate. In other words: the German government and Draghi’s ECB would be adversaries in a public court case.
Such a legal battle between the government and a central bank would be a first in German history. It could lead to a constitutional crisis of unprecedented severity or to currency turbulence — which is why it is extremely improbable that the two sides would allow the conflict to escalate to such a degree.
But the very fact that senior officials in the German Finance Ministry are considering their legal options makes it clear just how great the frustration with Draghi has become. The ECB head’s ever more imaginative ideas for increasing the money supply, say Finance Ministry officials, indicate that he is only concerned about the psyche of the international financial markets and not about average German savers.
The Concerns of Savers
Following the disastrous results of the three recent state elections in Germany — elections which saw the AfD succeed at the expense of Merkel’s Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and Gabriel’s SPD — the government in Berlin has different priorities. Particularly among German conservatives — a designation that includes the CDU as well as its Bavarian sister party, the Christian Social Union (CSU) — worries are growing that, with the refugee crisis abating, the AfD could turn its fury on the ECB. Such a shift could cost conservatives additional voters, particularly since the concerns of savers have long been a central issue for the CDU.
Conservative floor leader Volker Kauder, a close ally of Merkel’s, has warned against heaping too much pressure on the ECB. “It was the CDU and the CSU that insisted on central bank independence,” he says. “We should behave accordingly.”
But the mood in the party has clearly shifted. During a recent visit to his constituency, Kauder’s deputy, economics expert Michael Fuchs, experienced first-hand just how concerned voters are about the interest-rate issue. One enraged man screamed at him during an event that Merkel is to blame for the low interest rates. Such anger is fertile soil for the AfD. “On this issue, it isn’t easy to counter the AfD,” Fuchs says. “The criticism of the ECB is justified.” Merkel’s coalition, he says, “must clearly say that it finds Mr. Draghi’s interest rate policy to be incorrect. We haven’t been loud enough.”
That may soon change. The number of party allies joining in Fuchs’ critique has been growing in recent weeks. Following a joint meeting in Dresden, conservative finance experts from German state parliaments issued a statement saying that Draghi’s policies are undermining trust in the common currency. Ralph Brinkhaus, deputy head of the conservative party group in German parliament, says: “We have to pressure the ECB to justify its policies. Otherwise, nothing will change.”
The most pointed attacks have come from the Bavarian CSU. With the refugee crisis having faded into the background, party head Horst Seehofer has made his opposition to Draghi his next major issue. Bavarian Finance Minister Markus Söder has already set the tone: “The zero-interest policy is an attack on the assets of millions of Germans, who have placed their money in savings accounts and in life insurance policies,” he says.
Söder believes that emphatic critique of the ECB will bring political benefits. The ECB may be independent, but it isn’t omnipotent, he says. “We need a debate in Germany about the erroneous policies of the ECB,” he says. “The German government must demand a change in direction on monetary policy. If things continue as they have, it will be a boon for the AfD.” Ahead of a July conclave of the Bavarian state cabinet, Söder has been charged with developing ideas for what can be done to counter Draghi’s course.
Source: Mario Brothers: Germany Takes Aim at the European Central Bank – Spiegel Online